Reliability study on establishing a rat tuberculosis wound model using Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
-
摘要:
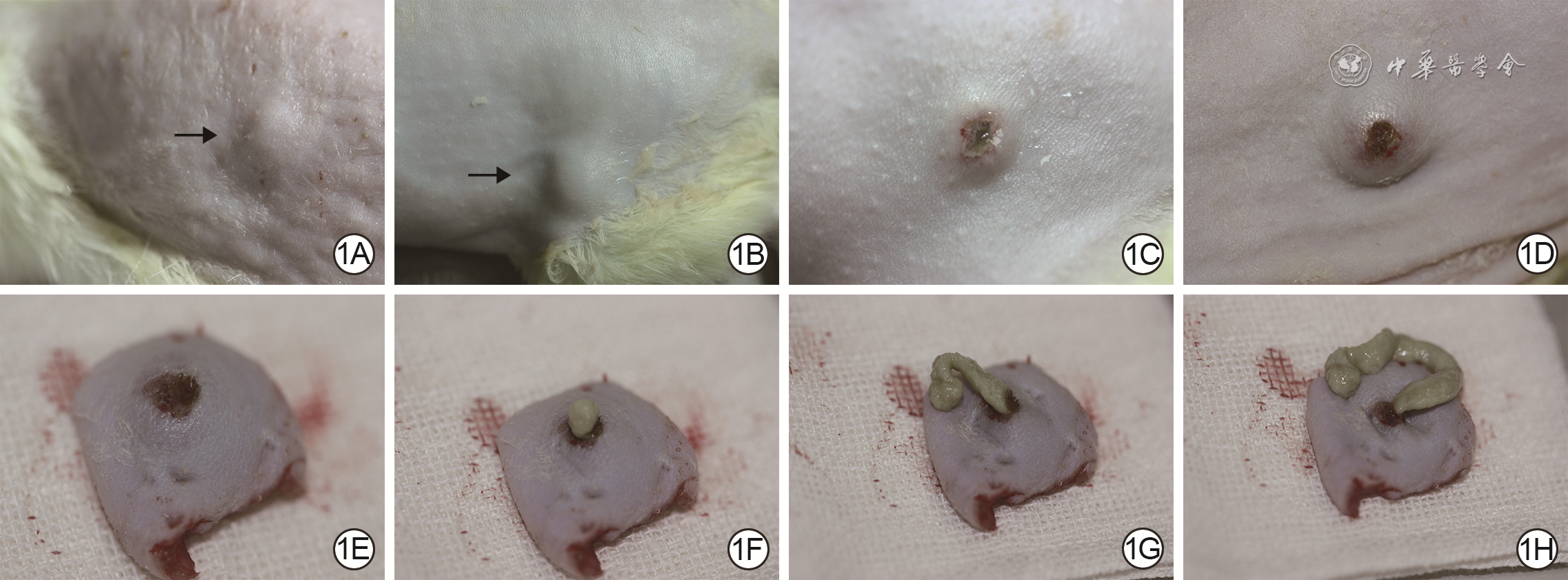
目的 探讨通过注射牛分枝杆菌减毒株(BCG)建立大鼠结核性创面模型的可靠性。 方法 采用实验研究方法。将15只6周龄雄性SD大鼠按照随机数字表法分为正常对照组和感染组,其中正常对照组3只、感染组12只。感染组大鼠在背部皮下注射弗氏完全佐剂3周后皮下注射BCG菌液,建立大鼠结核性创面模型;正常对照组不做任何处理。于感染第8、15、32、43天,大体观察感染组大鼠注射部位皮肤情况;于前述时间点分别取感染组3只大鼠注射部位皮肤组织,另取正常对照组大鼠对应部位皮肤组织,行苏木精-伊红染色,观察细胞排列、坏死及炎症等情况。对感染第43天感染组大鼠注射部位皮肤组织行抗酸染色,观察细菌分布情况。 结果 感染第8、15、32、43天,感染组大鼠注射部位皮肤逐渐形成结核性创面病灶,病变组织细胞排列杂乱或呈同心圆状,坏死细胞及肉芽肿数量逐渐增多;正常对照组大鼠对应部位的皮肤组织细胞排列规律,未见炎症细胞浸润。感染第43天,感染组大鼠注射部位皮肤组织中可见大量杆状细菌。 结论 使用BCG建立的大鼠结核性创面模型稳定可靠,可以满足实验要求。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the reliability of a rat tuberculous wound model established by injecting Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG). Methods The experimental research was conducted. According to the random number table, fifteen 6-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into normal control group and infection group, with 3 rats in normal control group and 12 rats in infection group. Rats in infection group were injected with Freund's complete adjuvant, 3 weeks later, they were injected subcutaneously with BCG bacterial solution to establish a model of tuberculous wounds in rats; rats in normal control group did not receive any treatment. On the 8th, 15th, 32nd, and 43rd day of infection, the skin condition at the injection sites of the rats in infection group was observed roughly. Skin tissue at the injection sites of 3 rats in infection group at each corresponding time point stated above and skin tissue at the corresponding sites of the rats in normal control group were stained with hematoxylin-eosin to observe the cell arrangement, necrosis and inflammation. On 43rd day of infection, acid-fast staining was performed on the skin tissue at the injection sites of the rats in infection group to observe the distribution of bacteria. Results On the 8th, 15th, 32nd, and 43rd day of infection, tuberculous wound lesions were gradually developed at the skin tissues at the injection sites of the rats in infection group. The cells of the diseased tissue of the rats in infection group arranged disorderly or concentrically, and the number of granulomas and necrotic cells gradually increased, while the skin tissue cells in the corresponding parts of the rats in normal control group arranged regularly with no inflammatory cell infiltration. On the 43rd day of infection, a large number of rod-shaped bacteria were observed in the skin tissue at the injection sites of the rats in infection group. Conclusions The rat tuberculous wound model established using BCG is stable and reliable, which can meet the experimental requirements. -
Key words:
- Models, animal /
- Tuberculosis, cutaneous /
- Rats /
- Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
-
参考文献
(23) [1] World Health Organization Global tuberculosis report 2020-05-31 https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/data World Health Organization.Global tuberculosis report[R/OL].2018[2020-05-31]. https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/data.
[2] World Health Organization Global tuberculosis report 2020-05-31 https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/data World Health Organization.Global tuberculosis report[R/OL].2017[2020-05-31]. https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/data.
[3] 贾赤宇.结核性创面——一个被忽视且值得重视的临床问题[J/CD].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2014,9(4):9-11.DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1673-9450.2014.04.003. [4] SahinN,AydinNE,SenolM,et al.Longstanding skin ulcers due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a healthy man[J].Trop Biomed,2010,27(1):120-124. [5] 荣美玉,贾赤宇.单中心结核性创面与非结核性慢性难愈性创面患者的特点[J].中华烧伤杂志,2019,35(2):90-94.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.02.003. [6] 常娜,贾赤宇,刘真,等.235例肺外结核性创面患者流行病学调查[J].中华烧伤杂志,2015,31(2):122-124.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2015.02.011. [7] 贾赤宇,李鹏程,程琳,等.外科干预治疗模式在窦道型结核性创面中的临床应用[J].中华烧伤杂志,2016,32(6):326-330.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.06.003. [8] 吕晓武,贾赤宇,冯胜娟,等.胸壁结核性创面外科治疗进展[J].感染、炎症、修复,2014,15(2):122-124.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8521.2014.02.021. [9] 秦云贺,王艺红,郭庆龙,等.结核分枝杆菌菌悬液光密度值与菌落计数的关联性[J].中国感染控制杂志,2016,15(3):150-154.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9638.2016.03.002. [10] DannenbergAM.Liquefaction and cavity formation in pulmonary TB: a simple method in rabbit skin to test inhibitors[J].Tuberculosis (Edinb),2009,89(4):243-247.DOI: 10.1016/j.tube.2009.05.006. [11] HusainAA,DaginawalaHF,WarkeSR,et al.Investigation of immune biomarkers using subcutaneous model of M. tuberculosis infection in BALB/c mice: a preliminary report[J].Immune Netw,2015,15(2):83-90.DOI: 10.4110/in.2015.15.2.83. [12] 张同威,汪毅平,贾赤宇.清创后外用碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对新西兰兔结核性创面愈合的影响[J].中华烧伤杂志,2019,35(2):95-103.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.02.004. [13] 汪毅平,刘真,张亚洁,等.结核性创面大鼠模型中巨噬细胞极化改变[J/CD].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2018,13(1):30-36.DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1673-9450.2018.01.007. [14] ChenL,LiuZ,SuY,et al.Characterization of Mycobacterium marinum infections in zebrafish wounds and sinus tracts[J].Wound Repair Regen,2017,25(3):536-540.DOI: 10.1111/wrr.12540. [15] ImamuraT,IyamaK,TakeyaM,et al.Role of macrophage tissue factor in the development of the delayed hypersensitivity reaction in monkey skin[J].Cell Immunol,1993,152(2):614-622.DOI: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1317. [16] 汪毅平,张同威,贾赤宇.结核性创面动物模型的研究进展[J/CD].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2017,12(4):309-311.DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1673-9450.2017.04.014. [17] ZhangG,ZhuB,ShiW,et al.Evaluation of mycobacterial virulence using rabbit skin liquefaction model[J].Virulence,2010,1(3):156-163.DOI: 10.4161/viru.1.3.11748. [18] DongX,LuoY,GaoQ,et al.Effects of MBL-associated serine protease-2 (MASP-2) on liquefaction and ulceration in rabbit skin model of tuberculosis[J].Microb Pathog,2016,99:282-286.DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.08.037. [19] 王明珠,史大中,杨爱军,等.分枝杆菌所致家兔皮肤液化病理模型研究[J].微生物与感染,2008,3(4):208-211,218.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6184.2008.04.004. [20] SugaM,DannenbergAM,HiguchiS.Macrophage functional heterogeneity in vivo. Macrolocal and microlocal macrophage activation, identified by double-staining tissue sections of BCG granulomas for pairs of enzymes[J].Am J Pathol,1980,99(2):305-323. [21] HiguchiS,SugaM,DannenbergAM,et al.Persistence of protein, carbohydrate and was components of tubercle bacilli in dermal BCG lesions[J].Am Rev Respir Dis,1981,123(4 Pt 1):397-401.DOI: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.4.397. [22] ChenH,LiuX,MaX,et al.A new rabbit-skin model to evaluate protective efficacy of tuberculosis vaccines[J].Front Microbiol,2017,8:842.DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00842. [23] GutierrezMG,MasterSS,SinghSB,et al.Autophagy is a defense mechanism inhibiting BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in infected macrophages[J].Cell,2004,119(6):753-766.DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.038. -
-








 下载:
下载: