Clinical effects of free transplantation of expanded ilioinguinal flaps in the reconstruction of severe scar contracture deformity after extensive burns
-
摘要:
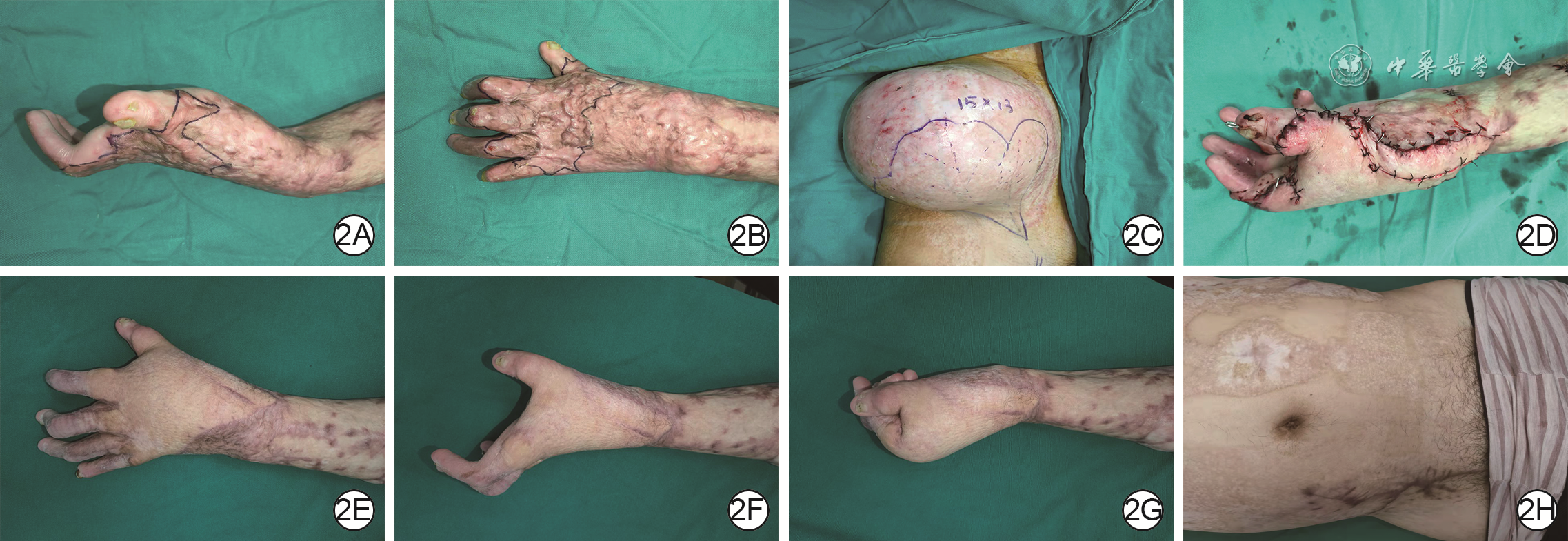
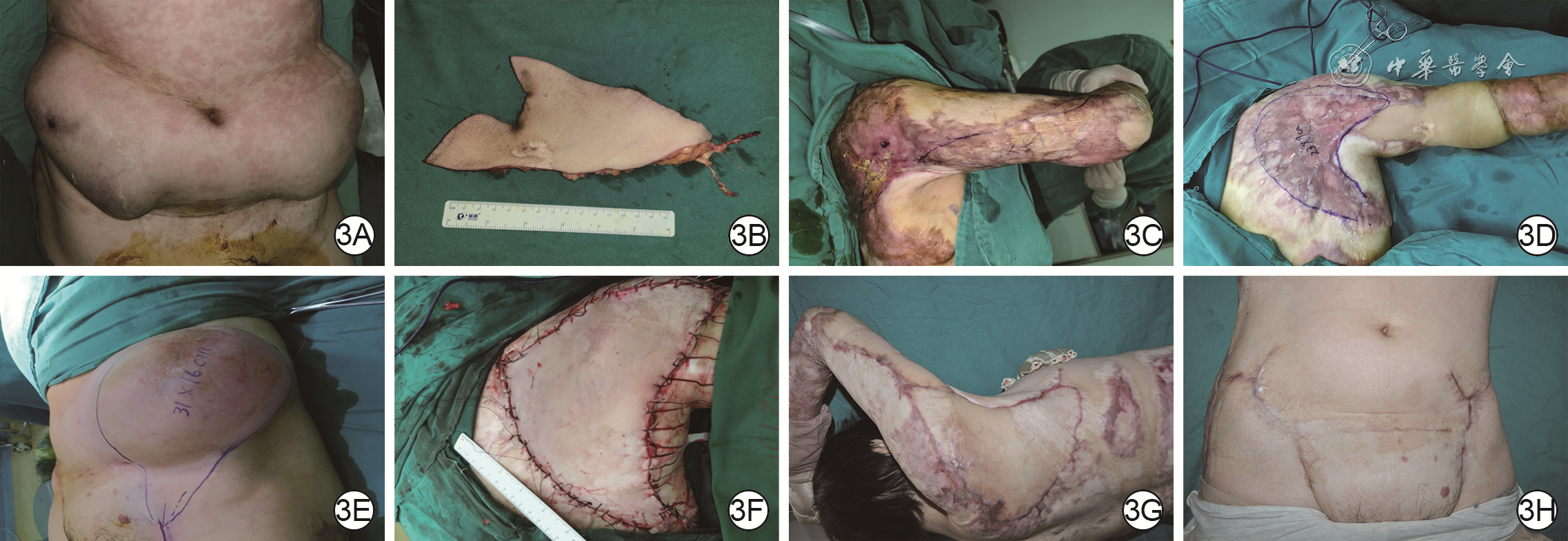
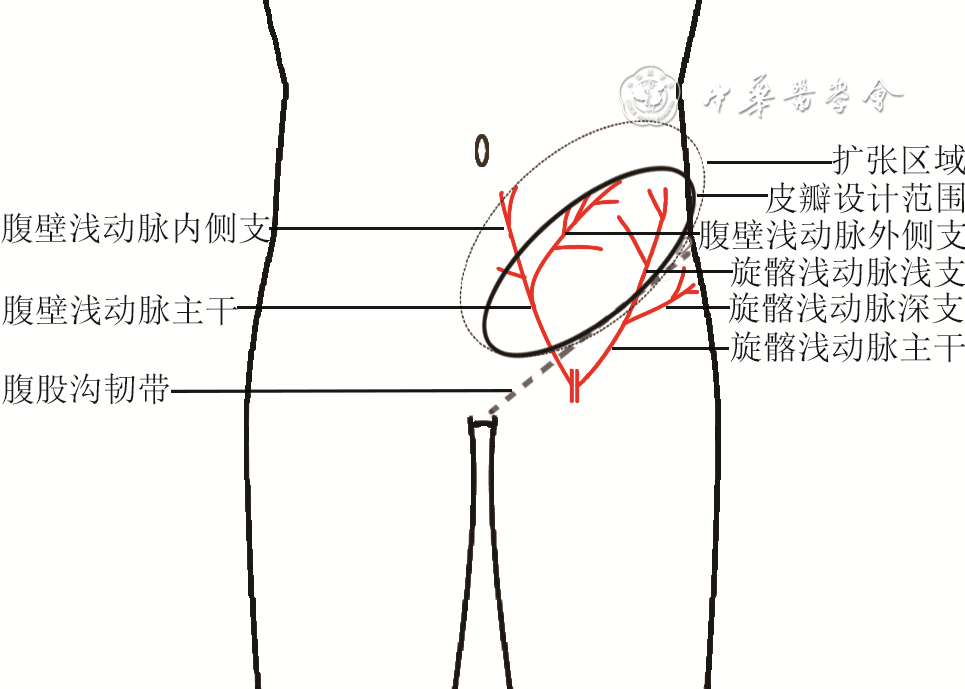
目的 探讨扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣游离移植整复大面积烧伤后严重瘢痕挛缩畸形的临床效果。 方法 采用回顾性观察性研究方法。2017年8月—2021年10月,武汉大学同仁医院暨武汉市第三医院收治7例大面积烧伤后严重瘢痕挛缩畸形患者,其中男5例、女2例,年龄26~65岁,瘢痕面积20 cm×4 cm~34 cm×14 cm。Ⅰ期于腹股沟韧带上方埋置额定容量为500~600 mL长方形皮肤软组织扩张器(以下简称扩张器),拆线后注射生理盐水扩张以满足修复手术需求。Ⅱ期手术切除瘢痕,矫正畸形,松解粘连及挛缩;取出扩张器后切取扩张髂腹股沟游离皮瓣,需较大皮瓣时联合切取脐旁穿支皮瓣,将皮瓣移植于瘢痕切除后继发创面。观察并记录扩张器埋置个数、注射生理盐水总量、扩张时间,皮肤软组织扩张术并发症发生情况,切取扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣个数、面积、厚度、吻合血管蒂,采用皮瓣类型,供瓣区修复方法,术后皮瓣成活情况。随访远期修复效果及供区情况,于末次随访时参照李克特量表5级评分调查患者对每个手术部位的疗效满意度。 结果 7例患者共埋置10个扩张器,其中4例患者各埋置1个,3例患者各埋置2个。注射生理盐水总量为800~1 800(1 342±385)mL,扩张时间为4~24(11±5)个月。1例患者置入扩张器后因感染致扩张器外露,其余患者未发生皮肤软组织扩张术并发症。切取扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣个数为10个,面积为22 cm×6 cm~36 cm×16 cm[(326±132)cm2],厚度为0.6~1.1(0.77±0.16)cm。10个扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣中,5个以旋髂浅动脉为蒂,3个以口径相对较大的腹壁浅动脉为蒂,1个以旋髂浅动脉和腹壁浅动脉共干为蒂,1个皮瓣吻合旋髂浅动脉的同时桥接腹壁浅动脉做动脉内增压。4例患者联合切取单侧扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣与同侧脐旁穿支皮瓣,1例患者联合切取双侧扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣,2例患者仅切取单侧扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣。除1例患者联合切取双侧扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣后供瓣区移植自体刃厚头皮修复外,其余患者供瓣区均直接缝合。术后皮瓣全部成活,无尖端坏死,无创面残留。随访3~30(15±10)个月,皮瓣质地柔软且不臃肿,受区功能、外观均较术前有明显改善,供区外观良好。末次随访时,患者对手术部位治疗效果的满意度评分为4~5(4.5±0.4)分。 结论 扩张髂腹股沟皮瓣可获取面积大,具有血运丰富、供区损伤小、位置隐蔽、便于联合脐旁穿支皮瓣切取移植等优势,适合用于大面积烧伤后严重瘢痕挛缩畸形的临床整复治疗。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical effects of free transplantation of expanded ilioinguinal flaps in the reconstruction of severe scar contracture after extensive burns. Methods A retrospective observational study was conducted. From August 2017 to October 2021, 7 patients with severe scar contracture deformity caused by extensive burns were hospitalized in Tongren Hospital of Wuhan University & Wuhan Third Hospital, including 5 males and 2 females, aged 26-65 years, with scar area of 20 cm×4 cm-34 cm×14 cm. In the first stage, the rectangular skin and soft tissue expander (hereinafter referred to as the expander) with rated capacity of 500-600 mL were embedded above the inguinal ligament, and then normal saline was injected after stitch removal for expansion to meet the needs of repair surgery. In the second stage, the scar was removed by surgical excision to correct the deformity and release the adhesion and contracture; after the removal of the expanders, the expanded ilioinguinal free flaps were harvested. When a larger flap was needed, the paraumbilical perforator flap was harvested at the same time, and the flaps were transplanted to the secondary wound after scar resection. The number of embedded expanders, the total amount of injected normal saline, the expansion time, the complications of skin and soft tissue expansion, the number, area, thickness, and anastomotic vascular pedicles of the expanded ilioinguinal flaps being resected, the type of flaps used, the repair method of flap donor sites, and the survival of flaps after operation were observed and recorded. The long-term repair effect and donor site condition were followed up. At the last follow-up, the patients' satisfaction with the curative effect of each surgical site was investigated according to the grade 5 score of Likert scale. Results A total of 10 expanders were embedded in 7 patients, of which 4 patients had 1 each and 3 patients had 2 each. The total volume of normal saline injected was 800-1 800 (1 342±385) mL, and the expansion time was 4-24 (11±5) months. One patient had the expander exposed due to infection after the expander being inserted, while the other patients had no complications of skin and soft tissue expansion. Totally 10 expanded ilioinguinal flaps with the area of 22 cm×6 cm-36 cm×16 cm ((326±132) cm2) and the thickness of 0.6-1.1 (0.77±0.16) cm were harvested. Among the 10 expanded ilioinguinal flaps, 5 were pedicled with the superficial circumflex iliac artery, 3 with the superficial abdominal artery with relatively large caliber, 1 with the common trunk of the superficial circumflex iliac artery and the superficial abdominal artery, and 1 flap was anastomosed with the superficial circumflex iliac artery and bridged the superficial abdominal artery for intra-arterial supercharge. Unilateral expanded ilioinguinal flap combined with ipsilateral paraumbilical perforator flap were harvested in 4 cases, bilateral expanded ilioinguinal flaps were harvested in 1 case, and unilateral expanded ilioinguinal flap was harvested in 2 cases. Except for 1 case being transplanted with autologous split-thickness scalp to repair the flap donor site after combined resection of bilateral expanded ilioinguinal flaps, the donor sites of the other patients were sutured directly. All the flaps survived after operation without tip necrosis or wound residue. Follow-up for 3-30 (15±10) months showed that the flap was soft and not bloated, the function and appearance of the recipient area were significantly improved compared with those before operation, and the appearance of the donor sites was good. At the last follow-up, the patients' satisfaction with the treatment effect of the surgical site scored 4-5 (4.5±0.4). Conclusions The expanded ilioinguinal flap can be obtained in a large area. It has the advantages of rich blood supply, less damage to the donor site, concealed location, and being convenient to be resected and transplanted in combination with the paraumbilical perforator flap. It is suitable for the clinical reconstruction and treatment of severe scar contracture deformity after extensive burns. -
Key words:
- Burns /
- Cicatrix /
- Contracture /
- Dilatation /
- Surgical flaps /
- Free flap /
- Ilioinguinal region
-
陈斓:手术操作、数据整理以及论文撰写;张伟、谢卫国:手术操作、论文撰写、研究指导、论文修改、经费支持;杨飞:手术操作、论文撰写;李泽:数据整理、统计学分析所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
-
参考文献
(31) [1] 彭君强,李养群,赵穆欣,等.皮肤软组织扩张术修复四肢大面积瘢痕的效果[J].中华烧伤杂志,2019,35(4):308-310.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.04.011. [2] 沈余明.深度烧伤后瘢痕增生挛缩畸形的手术治疗[J].中华烧伤杂志,2019,35(6):401-404.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.06.001. [3] OgawaR. Surgery for scar revision and reduction: from primary closure to flap surgery[J/OL]. Burns Trauma,2019,7:7 [2022-02-10].https://pubmed.keketh.cn/30891462/.DOI: 10. 1186/s41038-019-0144-5. [4] 马显杰, 丁健科. 皮肤软组织扩张术在儿童体表病损修复中的应用[J]. 中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022, 38(4): 301-305. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20211019-00359. [5] 胡骁骅,覃凤均,李娟,等.穿支皮瓣整复严重烧伤患者四肢大关节部位瘢痕增生挛缩畸形的效果[J].中华烧伤杂志,2019,35(6):417-422.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.06.004. [6] 夏成德,薛继东,狄海萍,等.额顶部跨中线轴型扩张皮瓣单蒂转移整复面颈部大面积瘢痕畸形的临床效果[J].中华烧伤杂志,2020,36(9):838-844.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200311-00149. [7] PukancsikD,KelemenP,GulyásG,et al.Clinical experiences with the use of ULTRAPRO® mesh in single-stage direct-to-implant immediate postmastectomy breast reconstruction in 102 patients: a retrospective cohort study[J].Eur J Surg Oncol,2017,43(7):1244-1251.DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.01.236. [8] McGregorIA,JacksonIT.The groin flap[J].Br J Plast Surg,1972,25(1):3-16.DOI: 10.1016/s0007-1226(72)80003-1. [9] 王海文.腹股沟皮瓣的形式及其临床应用[J].中华显微外科杂志,2020,43(2):205-208,C1-C3.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441206-20200213-00054. [10] GohTLH,ParkSW,ChoJY,et al.The search for the ideal thin skin flap: superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator flap--a review of 210 cases[J].Plast Reconstr Surg,2015,135(2):592-601.DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000951. [11] HongJP,SunSH,Ben-NakhiM.Modified superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator flap and supermicrosurgery technique for lower extremity reconstruction: a new approach for moderate-sized defects[J].Ann Plast Surg,2013,71(4):380-383.DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3182503ac5. [12] 中国整形美容协会瘢痕医学分会.瘢痕早期治疗全国专家共识(2020版)[J].中华烧伤杂志,2021,37(2):113-125.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200609-00300. [13] 马显杰,李威扬,刘超华,等.面部烧伤后瘢痕的美学整复策略及疗效[J].中华烧伤杂志,2016,32(8):469-473.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.08.006. [14] 张伟,谢卫国,张卫东,等.吻合血管的扩张皮瓣治疗大面积烧伤患者瘢痕挛缩畸形[J].中华烧伤杂志,2019,35(6):410-416.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.06.003. [15] 杜伟力,沈余明,胡骁骅,等.供瓣区美学修复方法的探讨[J].中华烧伤杂志,2020,36(2):97-105.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2020.02.004. [16] HocaoğluE,EmeklıU,ÇızmecıO,et al.Suprafascial pre-expansion of perforator flaps and the effect of pre-expansion on perforator artery diameter[J].Microsurgery,2014,34(3):188-196.DOI: 10.1002/micr.22184. [17] WangC,YangS,PuLL.Pre-expanded super-thin skin perforator flaps[J].Clin Plast Surg,2017,44(1):31-40.DOI: 10.1016/j.cps.2016.08.008. [18] AtikB,TanO,CeylanK,et al.Reconstruction of wide scrotal defect using superthin groin flap[J].Urology,2006,68(2):419-422.DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.04.003. [19] 孙广峰,魏在荣,金文虎,等.扩张髂腹股沟超薄皮瓣修复手部前臂瘢痕[J].中华手外科杂志,2015,31(1):53-55.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-054X.2015.01.020. [20] 郑捷新,张勤,刘琰,等.大面积烧伤瘢痕的后期整复治疗[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2010,30(5):600-603. [21] 孙广峰,聂开瑜,邓呈亮,等.游离旋髂浅动脉穿支皮瓣修复足踝部皮肤软组织缺损[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(11):1396-1399.DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.20160287. [22] 刘林峰,臧成五,丛锐.应用旋髂浅动脉浅支为蒂的穿支皮瓣修复手部皮肤缺损[J].中华手外科杂志,2020,36(2):140-141.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311653-20190628-00186. [23] 贾颖,王铁铮,刘林峰,等.旋髂浅动脉皮瓣血管的解剖与超声评价[J].医学影像学杂志,2020,30(3):486-488. [24] KashiwaK,KobayashiS,SaitoA,et al.Inferior extension of the groin flap based on the descending branch of the superficial circumflex iliac artery[J].J Reconstr Microsurg,2002,18(8):653-658.DOI: 10.1055/s-2002-36495. [25] SinnaR,HajjiH,QassemyarQ,et al.Anatomical background of the perforator flap based on the deep branch of the superficial circumflex iliac artery (SCIP flap): a cadaveric study[J].Eplasty,2010,10:e11. [26] 寇伟,胡勇,朱磊,等.游离髂腹股沟皮瓣在手足创面修复中的应用[J].中华显微外科杂志,2013,36(4):400-402.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2013.06.032. [27] 王晓敏,马士崟,张凯,等.腹壁浅动脉皮瓣的应用解剖及其在头颈部修复中的意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2011,29(4):378-381. [28] 韩军涛,谢松涛,陶克,等.旋髂浅动脉岛状分叶皮瓣修复下腹部及会阴区瘢痕挛缩22例[J].中华烧伤杂志,2012,28(2):153-154.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2012.02.022. [29] 喜雯婧,冯少清,李华,等.旋髂浅动脉穿支皮瓣的重新评价和手术策略[J].中华显微外科杂志,2018,41(4):313-318.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2018.04.001. [30] 李广学,穆籣,杨锴,等.吲哚菁绿血管造影在腹部皮瓣乳房再造中的应用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2018,34(7):522-525.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-4598.2018.07.007. [31] KhoongYM,HuangX,GuS,et al.Imaging for thinned perforator flap harvest: current status and future perspectives[J/OL].Burns Trauma,2021,9:tkab042[2022-02-10].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34926708/.DOI: 10.1093/burnst/tkab042. -
-








 下载:
下载: