A case of multiple difficult illnesses in a patient with extremely severe burn complicated with type 2 diabetes
-
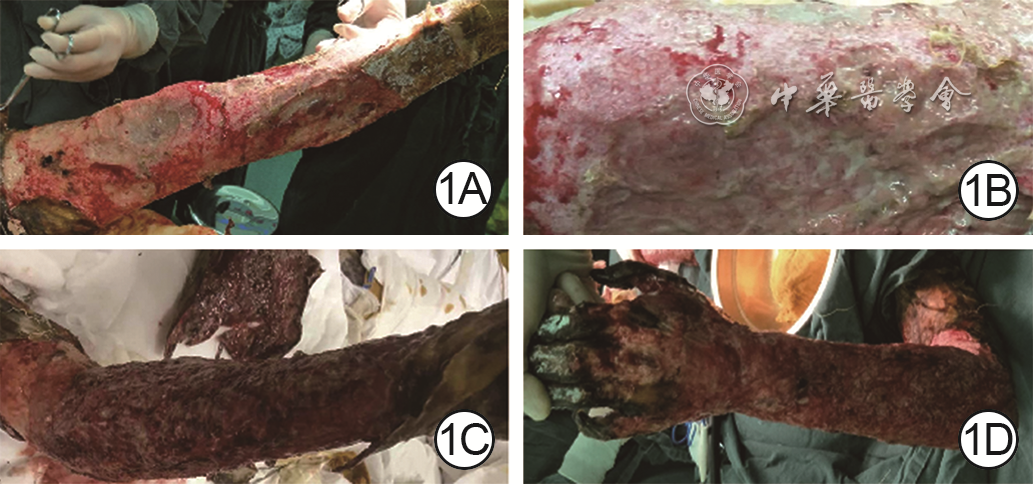
摘要: 2018年12月20日,广州市第一人民医院收治1例特重度火焰烧伤40岁男性患者,多种疑难病症同时(顽固性高血糖、顽固性高钠血症、创面进行性加深)或序贯(反复术后低血压、神经系统病变、继发性尿崩症)发生。患者入院后历经抗休克、降血糖、降血钠、削痂、分次植皮等治疗,仍于5个月后在高血糖、高血钠基本纠正、创面基本修复的情况下,因神经系统病变和继发性尿崩症而死亡。虽然上述病症未被完全明确病因,但是该团队采取针对性对症治疗措施以改善患者临床症状,维持内环境稳定及生理机能,加快创面修复进程的做法或许能为此类重症患者的治疗提供一些经验。Abstract: On December 20, 2018, a 40-year-old male patient with extremely severe flame burn was admitted to Guangzhou First People's Hospital. A variety of difficult illnesses occurred simultaneously (refractory hyperglycemia, refractory hypernatremia, and progressive wound deepening) and successively (repeatedly postoperative hypotension, nervous system diseases, and secondary diabetes insipidus). The patient underwent treatments such as anti-shock, reducing blood sugar and blood sodium, scab removing, and gradual skin grafting after admission. Although the hyperglycemia and hypernatremia were basically corrected and the wounds were basically repaired, the patient ultimately died of nervous system diseases and secondary diabetes insipidus 5 months later. Although the cause of the above illnesses can not be fully determined, the targeted treatments to improve clinical symptoms, maintain stable internal environment and physiological function, and accelerate the process of wound repair conducted by the team may provide some experience for the treatment of such severe patients.
-
Key words:
- Burns /
- Hyperglycemia /
- Hypernatremia /
- Hypotension /
- Diabetes insipidus /
- Complications
-
参考文献
(16) [1] 孙海伟,毛自若,周保纯,等.特重度烧伤患者预后影响因素的COX回归分析[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2021,30(1):89-92.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2021.01.018. [2] 刘虎仙,贾赤宇.胰岛素及血糖调控与烧伤创面愈合[J].中华烧伤杂志,2005,21(3):232-234.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2005.03.043. [3] 杨瑞凤,刘慧宁,于丽,等.血液净化技术在特重度烧伤严重并发症患者救治中的应用[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2019,20(11):1005-1006.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-587X.2019.11.022. [4] 吕磊,张兆新.重度烧伤并发高钠血症行CRRT治疗后死亡因素分析[J].西南国防医药,2014,24(9):941-943.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2014.09.005. [5] 刘谊蓉,马峰,周美兰,等.连续性静脉-静脉血液滤过治疗重度烧伤合并急性重度高钠血症[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2016,25(1):35-39.DOI: 10.3969/cndt.j.issn.1006-298X.2016.01.007. [6] 蔺枢勇.应用低钠透析治疗重度烧伤后合并高钠血症观察[J].中国中医药科技,2014,21(z1):177. [7] Aguayo-BecerraOA,Torres-GaribayC,Macías-AmezcuaMD,et al.Serum albumin level as a risk factor for mortality in burn patients[J].Clinics (Sao Paulo),2013,68(7):940-945.DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2013(07)09. [8] 王韶华,陈昭宏.大面积烧伤并发高钠血症一例[J].中华烧伤杂志,2016,32(7):440-441.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.07.015. [9] 董士华,曲狄,王雪莹,等.螺内酯治疗大面积烧伤合并高钠高氯血症的临床研究[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(13):130-131.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8194.2012.13.091. [10] 李翠萍,闫博.ICU内高钠血症发生的原因及合理治疗的方法探讨[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(3):102-103.DOI: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2015.03.068. [11] 易海清,曾丽珍.高浓度快速静脉补钾在特重度烧伤低钾血症护理中的应用[J].全科护理,2011,9(9):2385-2386.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4748.2011.026.024. [12] 王霖佳,吴建博,张云轩,等.注射用托拉塞米致老年住院患者低钾血症危险因素分析[J].中国临床医生杂志,2023,51(3):284-286.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2023.03.008. [13] 臧芝栋,严正,惠皎洁,等.平均血糖波动幅度对严重烧伤患者预后的意义[J].中华烧伤杂志,2016,32(1):35-39.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.01.010. [14] 左璐,李伟人,鲁加祥,等.严重烧伤后早期大鼠血糖测量方法探讨[J].中华内分泌外科杂志,2016,10(6):483-486.DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6090.2016.06.010. [15] 张驰,谢举临,田宜肥,等.高血糖水平对中度至极重度烧伤患者内皮细胞功能的影响[J].广东医学,2016,37增刊:63-66. [16] SugitaM,SugitaH,KimM,et al.Inducible nitric oxide synthase deficiency ameliorates skeletal muscle insulin resistance but does not alter unexpected lower blood glucose levels after burn injury in C57BL/6 mice[J].Metabolism,2012,61(1):127-136.DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.06.001. -
-








 下载:
下载: